The Caesar cipher is a classic method in cryptography to encode (encryption) and decode (decryption) text messages. The method is named after Julius Caesar, who used it in his private correspondence with his generals.
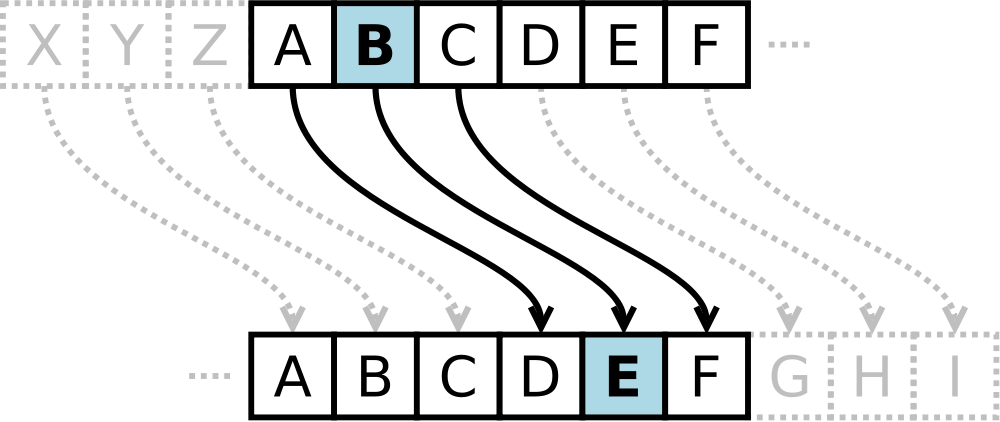
Encryption is executed by replacing each letter in the plain text by a letter some fixed number of positions down the alphabet. In doing this, the alphabet is considered to be circular, meaning that the letter Z is again followed by the letter A. Hence, also terms rotation or shift are used for this operation. For example, in rot3 (a rotation over three positions) the letter B is replaced during encryption by the letter E.
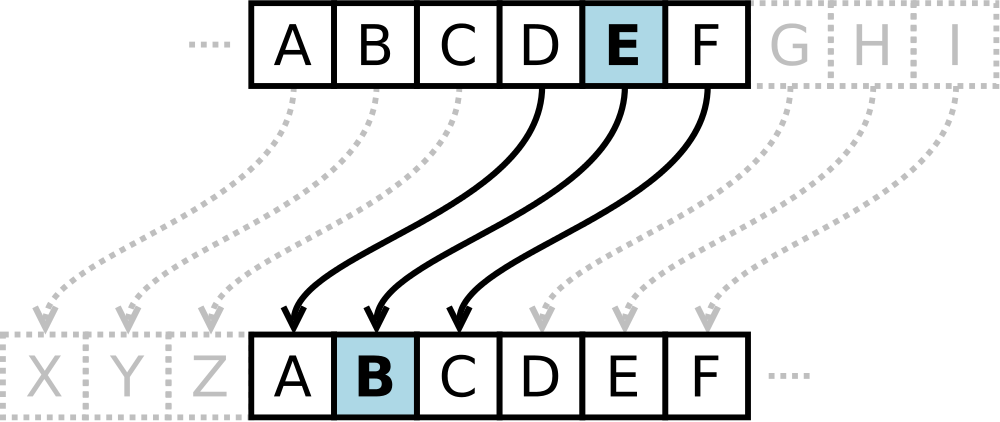
Deciphering a text message is done using the reverse operation. In this case a rotation or shift is performed to the left, instead of to the right as during encryption. For example, in rot3 the letter E is replaced during deciphering by the letter B.
Input
The first line of the input contains a number $$n \in \mathbb{N}$$ that indicates the number of positions a text is rotated during execution of the Caesar cipher. This is followed by a line containing a sentence that was encrypted using a Caesar rotation over $$n$$ positions. During this encryption, only letters of the alphabet were rotated (both upper case and lower case letters). All other characters (digits, punctuation marks, spaces, …) have been kept unchanged in the encrypted text.
Output
The sentence in plain text.
Example
Input:
20
Ylluly boguhog ymn.Output:
Errare humanum est.