In ggplot2 we create graphs by adding layers. Layers can define
geometries, compute summary statistics, define what scales to use, or
even change styles. To add layers, we use the + operator, do not use the pipe operator %>%!
In general, a line of code will look like this:
Dataframe %\>% ggplot() +
LAYER 1 +
LAYER 2 +
… +
LAYER N
Usually, the first added layer defines the geometry. We want to make a scatterplot. What geometry do we use?
Taking a quick look at the cheat sheet, we see that the function used to
create plots with this geometry is geom_point.
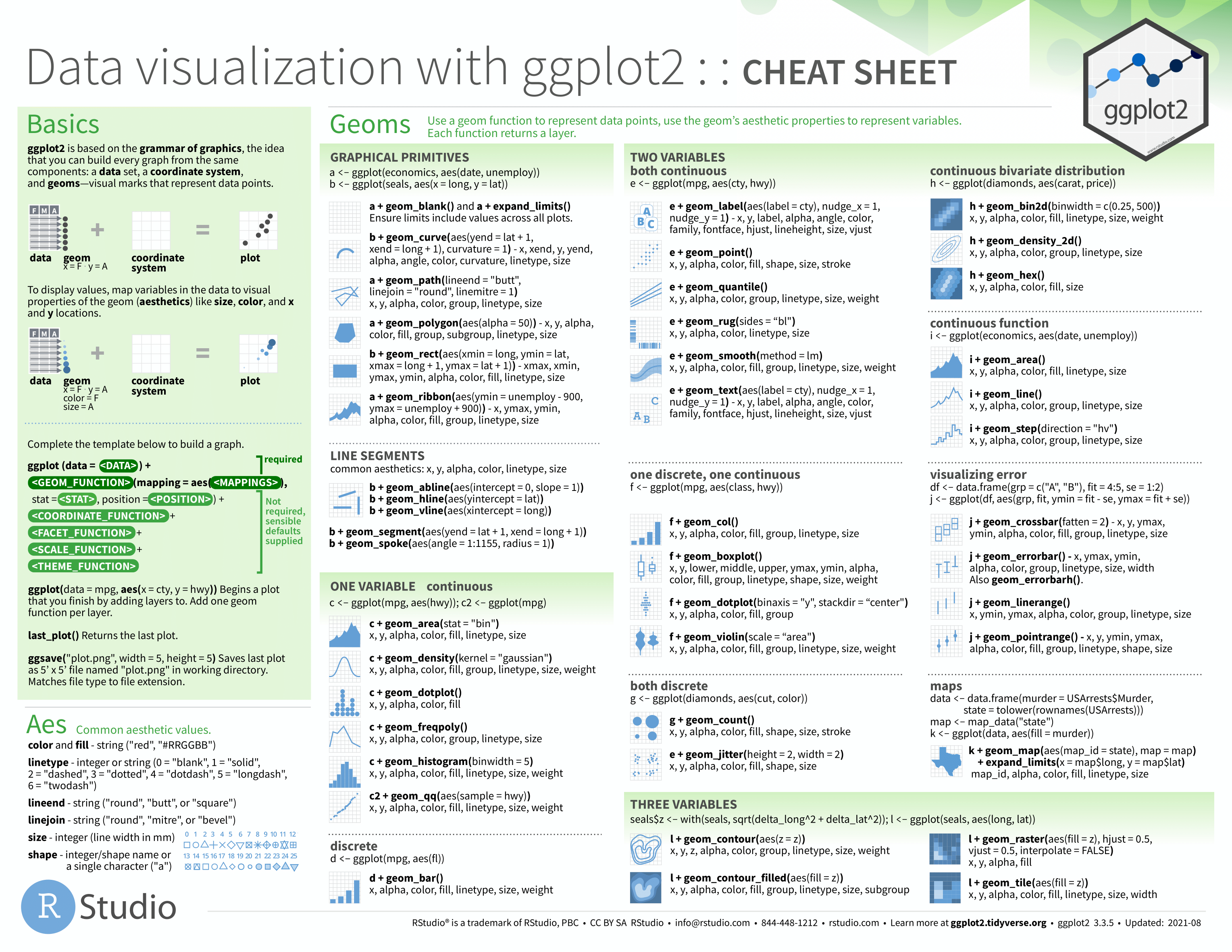
(Image courtesy of RStudio. CC-BY-4.0 license.)
Geometry function names follow the pattern: geom_X where X is the name
of the geometry. Some examples include geom_point, geom_bar, and
geom_histogram.
For geom_point to run properly we need to provide data and an aesthetics mapping.
We have already connected the object p with the murders data table,
and if we add the layer geom_point it defaults to using this data. To
find out what mappings are expected, we read the Aesthetics section
of the geom_point help file:
> Aesthetics
>
> geom_point understands the following aesthetics (required aesthetics are in bold):
>
> x
> y
> alpha
> colour
> fill
> group
> shape
> size
> stroke
and, as expected, we see that at least two arguments are required x
and y.