The Book of Common Prayer1 (1549) includes a Table of Kindred and Affinity2 that lists prohibited degrees of marriage in the Church of England3.

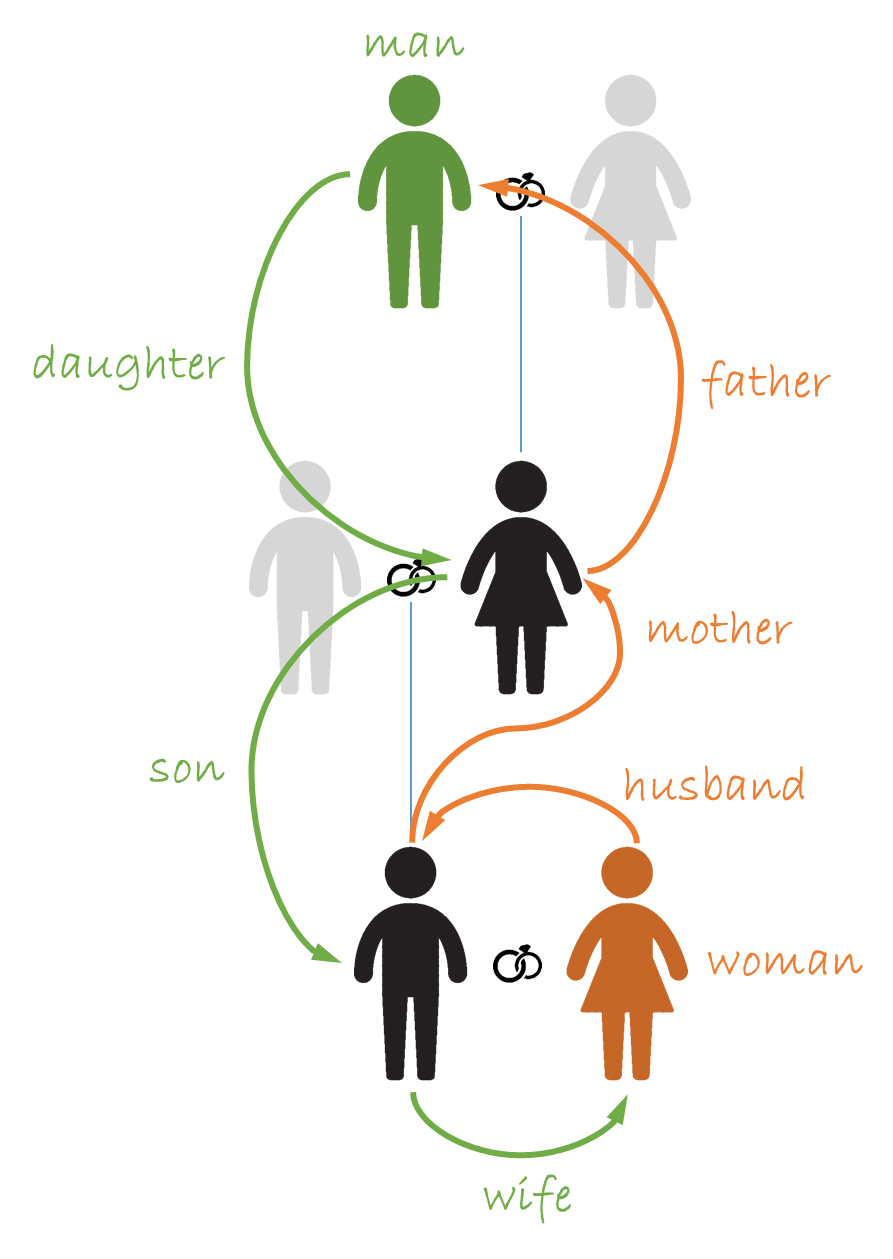
For example, a man may not marry his daughter's son's wife, and a woman may not marry her husband's mother's father. In this case, the two proscriptions correspond — they describe the same relationship "from both sides" — so this union is prohibited to both parties in the relationship. But is this always the case? Is each union that's denied to a man also denied to a woman? (The table only lists heterosexual unions.) It's not immediately clear: 25 prohibited degrees are listed for each sex, and our language makes it hard to "reverse" the description of a relationship mentally.
In 1989 mathematician M.D. Stern from the Manchester Metropolitan University4 worked out a binary notation for relationships between two people. This notation makes it easy to reverse the description of relationships. It uses the digit 1 to denote a male and the digit 0 to denote a female, and it uses the following codes to denote relations between individuals:
| code | type of relation | relation as a man (1) | relation as a woman (0) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 00 | spouse | husband (001) | wife (000) |
| 01 | parent | father (011) | mother (010) |
| 10 | child | son (101) | daughter (100) |
| 11 | sibling | brother (111) | sister (110) |
The notation of the relationship between two people starts with one digit for the first person (man = 1 and woman = 0), followed by three more digits for each successive relation — two digits (blue) to represent the type of relation and one digit (green) to represent the sex of the next person. So, taking the example above, a man's daughter's son's wife would be denoted as
1 100 101 000
To interpret the same relationship from the wife's point of view, we just need to reverse the order of the digits
0 001 010 011
He is her husband's mother's father.
Applying this to the prohibited degrees in the Table of Kindred and Affinity, Stern found that every prohibition for a man corresponds to an inverse prohibition for a woman. There are no prospective marriages that would be prohibited to one party but not to the other.
Assignment
In a marriage between two people, we drop the limitation to heterosexual marriages.
The description of a relationship between two people is a string (str) of the form
a (wo)man's (relation's )(relation's )(relation's )…relation
where one of the eight possible relations from the table in the introduction can be entered at the location of each relation. Parts in between round brackets are optional and the number of intermediate relations in the relationship is unlimited (as indicated by …).
The binary notation of a relationship between two people is a string (str) with $$1 + 3r$$ zeros (0) and ones (1), where $$r \in \mathbb{N}_0$$ is the number of intermediate relations in the relationship.
Your task:
-
Write a function description that takes the binary notation (str) of a relationship between two people. The function must return the description (str) of that relationship.
-
Write a function notation that takes the description (str) of a relationship between two people. The function must return the binary notation (str) of that relationship.
-
Write a function reverse_relationship that takes the description (str) of a relationship between two people. The function must return the description (str) of the reverse relationship.
All functions may assume that their arguments are valid, without the need to check this explicitly.
Example
>>> description('1100101000')
"a man's daughter's son's wife"
>>> description('0001010011')
"a woman's husband's mother's father"
>>> notation("a man's daughter's son's wife")
'1100101000'
>>> notation("a woman's husband's mother's father")
'0001010011'
>>> reverse_relationship("a man's daughter's son's wife")
"a woman's husband's mother's father"
>>> reverse_relationship("a woman's sister's father's husband's son")
"a man's father's husband's daughter's sister"
Epilogue
The marriage notices5 in the Scots Magazine of January 1790 contains this curious entry:
At Newburn, near Newcastle, Mr William Dormand, to Miss Hannah Hoy, of that place. The ceremony was attended by the father, mother, brother, sister, aunt, nephew, two husbands, and two wives, and yet there were only four persons present at the marriage.
No explanation is given. How is such an arrangement possible?
We don't know for certain, but one option is that William married his maternal uncle's widow, Hannah. Hannah's brother (call him Fred) married William's widowed mother (call her Sue):
-
husbands: William and Fred
-
wives: Hannah and Sue
-
brother/sister: Hannah and Fred
-
aunt/nephew: William and Hannah
-
mother/father: Sue and Fred (if we say that Fred is the stepfather of William)