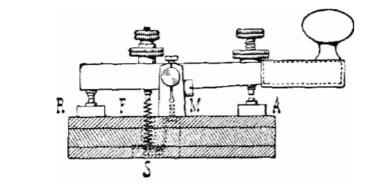
Morse code is a type of character encoding that transmits telegraphic information using rhythm. Morse code uses a standardized sequence of short and long elements to represent the letters, numerals, punctuation and special characters of a given message. Originally created for Samuel F. B. Morse’s electric telegraph (see image) in the early 1840s, morse code was also extensively used for early radio communication beginning in the 1890s. In the early part of the twentieth century, the majority of high-speed international communication was conducted in morse code, using telegraph lines, undersea cables, and radio circuits. However, the variable length of the morse characters made it hard to adapt to automated circuits, so for most electronic communication it has been replaced by machine readable formats, such as Baudot code and ASCII.
In international morse code, short signals are denoted using a dot (.) whereas long signals are denoted using a dash (-).
Opgave
The file morse.txt1 contains a list of words with their translation into morse code. Each line contains the morse code translation of a single word (inter-character breaks were not taken into account), followed by a space and the word itself in between brackets. You are asked to
-
Design regular expressions that match with the sets described below. In these descriptions, $$\mathcal{M}$$ represents the set of all words in morse code. Try to keep your regular expressions as short as possible.
-
$$\alpha = \{ m \in \mathcal{M}\,|\,$$ no symbol is consecutively repeated more than twice in $$m$$ $$\}$$
-
$$\beta = \{ m \in \mathcal{M}\,|\,$$ first and last two symbols in $$m$$ are the same, but in reversed order $$\}$$
-
$$\gamma = \{ m \in \mathcal{M}\,|\,$$ a dot occurs in all even positions of $$m$$ $$\}$$
-
$$\delta = \{ m \in \mathcal{M}\,|\,$$ $$m$$ has at least three and at most five dashes $$\}$$
Use a command from the grep family in order to select only those lines from the file morse.txt2 that belong to the given set.
-
-
Consider the sets $$\alpha$$, $$\beta$$, $$\gamma$$ and $$\delta$$ as defined above. Now, use these sets in order to find out the secret message that is composed of the following four words:
-
The first word is on the unique line with the morse code word belonging to $$\alpha \cap \beta$$
-
The second word is on the unique line with the morse code word belonging to $$\beta \cap \gamma$$
-
The second word is on the unique line with the morse code word belonging to $$\gamma \cap \delta$$
-
The second word is on the unique line with the morse code word belonging to $$\delta \cap \alpha$$
Indicate the Unix command (or command sequence) that was used to find each word. It is prohibited to literally enter the word (e.g.: echo xxx).
-