The square cells of a rectangular grid are filled with one of the building blocks below, forming a roadmap. The possible building blocks are (from left to right) i) empty cells, ii) cells with one junction (end points), iii) cells with two opposite junctions (straight lanes), iv) cells with two adjacent junctions (curves) and v) cells with four junctions (crossroads). Each of these building blocks can be rotated over an angle of 90°. This gives four possible end points, two possible straight lanes (horizontal and vertical) and four possible curves.
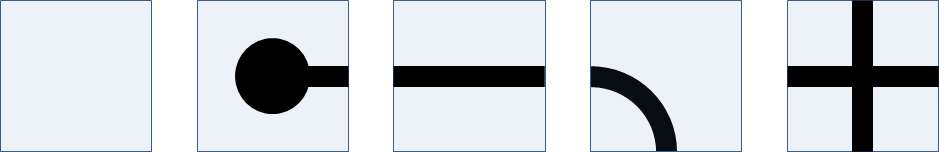
The roadmap is built in such a way that neighbouring cells always have adjacent junctions. Moreover, the roadmap map always links two ending points, if we always continue straight ahead at every crossroads. All ending points are indicated with a unique uppercase letter.
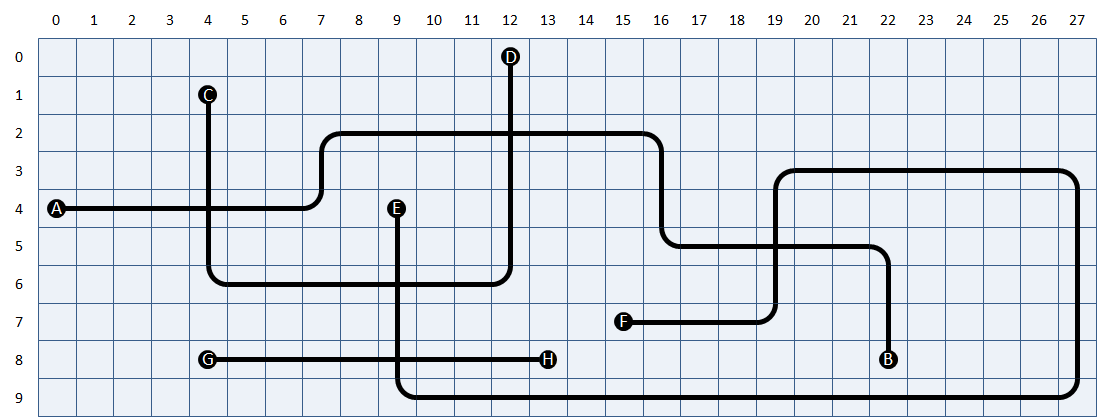
A roadmap with $$m$$ rows and $$n$$ columns can be saved in a text file of $$n$$ lines, that each consist of $$m$$ characters, as follows:
empty cells are represented by a space
ending points are represented by the uppercase letter that is used to indicate them
horizontal lanes are represented by a hyphen (-)
vertical lanes are represented by a vertical line (|)
both curves and crossroads are represented by a plus sign (+)
To determine whether a plus sign indicates a bow or a crossroads, you must verify the number of junctions a cell has with its neighbouring cells above, underneath, left and right. The file streetmap1.txt1, for example, contains the street map that was given as an example above.
Assignment
Define a class Streetmap that can be used to determine the positions of the ending points for a given street map that was saved in a text file, and which ending points are linked. The objects of the class must contain at least the following methods:
An initializing method to which the location of a text file can be passed. This text file must contain the representation of a street map.
A method rows (without arguments) that prints the number of rows from the street map.
A method columns (without arguments) that prints the number of columns from the street map.
A method location to which the uppercase letter from an ending point must be passed. The method must print a tuple that contains the row and column number of the cell in the grid on which the ending point is situated. Row and columns are numbered from zero, as indicated in the above example. If no ending point is situated in the street map that is indicated with the given uppercase letter, the method must raise an AssertionError with the message unknown end point.
A method connection to which the uppercase letter from an ending point must be given. The method must print the uppercase letter from the ending point with which the given ending point is linked by the street map. If no ending point can be found with the given uppercase letter in the street map, the method must raise an AssertionError with the message unknown end point.
Example
For the below example session, we assume that the files streetmap1.txt2 and streetmap2.txt3 are in the current directory.
>>> map = RoadMap('roadmap1.txt')
>>> map.rows()
10
>>> map.columns()
28
>>> map.location('A')
(4, 0)
>>> map.location('F')
(7, 15)
>>> map.connection('A')
'B'
>>> map.connection('B')
'A'
>>> map.connection('C')
'D'
>>> map.connection('D')
'C'
>>> map.connection('E')
'F'
>>> map.connection('F')
'E'
>>> map.connection('G')
'H'
>>> map.connection('H')
'G'
>>> map.connection('X')
Traceback (most recent call last):
AssertionError: unknown end point
>>> map = RoadMap('roadmap2.txt')
>>> map.connection('A')
'B'
>>> map.connection('B')
'A'
>>> map.connection('C')
'D'
>>> map.connection('D')
'C'
>>> map.connection('E')
'F'
>>> map.connection('F')
'E'
>>> map.connection('G')
'H'
>>> map.connection('H')
'G'
>>> map.connection('X')
Traceback (most recent call last):
AssertionError: unknown end point