The second nucleic acid
In "Counting DNA nucleotides", we described the primary structure of a nucleic acid as a polymer of nucleotide units, and we mentioned that the omnipresent nucleic acid DNA is composed of a varied sequence of four bases.
Yet a second nucleic acid exists alongside DNA in the chromatin. This molecule, which possesses a different sugar called ribose, came to be known as ribose nucleic acid, or RNA. RNA differs further from DNA in that it contains a base called uracil in place of thymine. Structural differences between DNA and RNA are shown in the figure below. Biologists initially believed that RNA was only contained in plant cells, whereas DNA was restricted to animal cells. However, this hypothesis dissipated as improved chemical methods discovered both nucleic acids in the cells of all life forms on Earth.
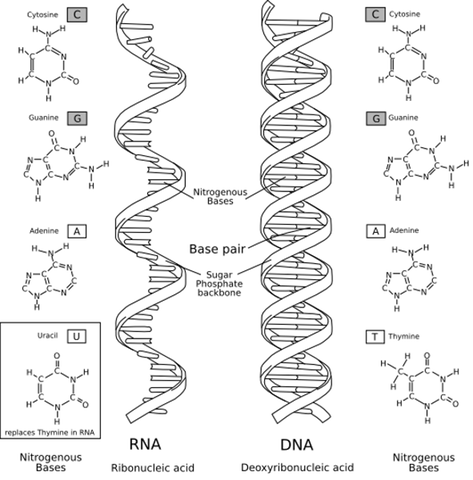
The primary structure of DNA and RNA is so similar because the former serves as a blueprint for the creation of a special kind of RNA molecule called messenger RNA, or mRNA. mRNA is created during RNA transcription, during which a strand of DNA is used as a template for constructing a strand of RNA by copying nucleotides one at a time, where uracil is used in place of thymine.
In eukaryotes, DNA remains in the nucleus, while RNA can enter the far reaches of the cell to carry out DNA's instructions. In future problems, we will examine the process and ramifications of RNA transcription in more detail.Assignment
An RNA string is a string formed from the alphabet containing A, C, G, and U. Given a DNA string $$s_{\textrm{DNA}}$$ corresponding to a coding strand, its transcribed RNA string $$s_{\textrm{RNA}}$$ is formed by replacing all occurrences of T in $$s_{\textrm{DNA}}$$ with U in $$s_{\textrm{RNA}}$$.
Write a function transcribe that takes a DNA string $$s_{\textrm{DNA}}$$. The function must return the transcribed RNA string $$s_{\textrm{RNA}}$$ of $$s_{\textrm{DNA}}$$.
Example
In the following interactive session, we assume the FASTA file data.fna to be located in the current directory.
>>> transcribe('GATGGAACTTGACTACGTAAATT') 'GAUGGAACUUGACUACGUAAAUU' >>> from Bio import SeqIO >>> transcribe(*SeqIO.parse('data.fna', 'fasta')) 'GCGGAUUCGACCCACUCGCUCUAGACUCUGCUACUUGCCUGUUGCAGCCGUUCGUAGAUAAGUAGGUGGUCCGGGUGCCCAGCACUAAUGUGGCAGGUAGGCAGCCAGGUGGUCUUUACAUGACGUCGUGAUCCAUGAUACAAGGACCGAAUGGUCACAGGGUGGCAGCAGGCUACCGAAAUGUCAUCUGGCUGCGGAAAACUAUGGAUAGUUACUAGACCAUUUAUCCAUGGGGACCAAUCCAGGUGCUUCAUUGACUACACCGGGAGUGCUUGCGUUCAAACCUGCCACGGGUGUAUGUGACACUAACGUAUUGUGGCUAGUUUUUUAACCUUCGAUCACGUCAGUGCCGAAUCAAAAAUUAAAGAACGUGAUGUAGAUGGUAAACCAUGCGAGGGGUCGGCUCAAGCAACACGGGUCACAACUCCCCCACCACGUUUAGAGUUCAUACCUUACGUAACUGGAAAUAGUGUCGAGUGAUCUGAUGAGUACGCAUGCAAACAAAAGACGAGGGCUUAAUUCGGAAGUUCUACCCCCAGGAGCGACUUAAGUGUGAUAUGCCCUAUUACUUGUUCAGUACACAGUAUAGUCAGAGGAGGAACUGCGUAAAUGGCGGGACCACUACCUAGUCCCAGCCUGCGACCACGCCAAUGAGACCCCAACUGUCUUAAUGCACAUUCACGUGCCUCUUGUGCGUAGUCUAUGUAGGUCUUGUCCUGAGACCUUGACAGAUUAAUGUGUGUCGUCGGACUUUAUCGAUACAGGUAAGUCCCACCACUCGUUUGGUAGUGUCCAUCCCUCCGCCCUGAUUUCUCUAGCAAUCGCUCCGCAAUCUUUUACUACCCUCUCAGCGUGCGGCAAAUGAGCGUCACAUGGUUUCGAAGUGAUUACUAAUUAGUCUGAUGUCUUUACACAACGGGAGGAGGGUGUUGUUUGCCGAUGGCCGA'