In the contentious presidential election of 1876, the campaign of Democrat Samuel Tilden sent many enciphered messages to its agents in contested states.

Two years after the election, the New York Daily Tribune published some of the deciphered telegrams, showing that Tilden’s campaign had tried to bribe election officials to win the race. Here’s one of the telegrams:

Since only 10 letters are used, it seems likely that the cipher refers to pairs of letters (bigrams). So if each successive pair in the message is assigned to an arbitrary letter

then we have a simple cryptogram that can be solved to give the message:

Tilden’s campaign did the same thing with pairs of numbers. For example, this message
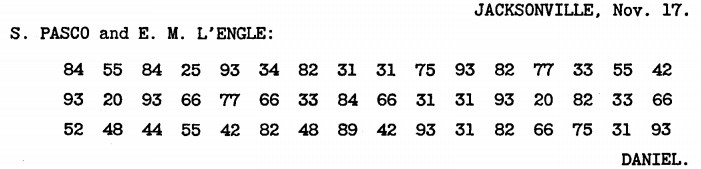
turns out to mean:

In 1879 the Tribune’s experts worked out the letter and number pairs that had corresponded to each letter of the alphabet:

But it was not until 1952 that cryptographer William F. Friedman reconstructed the table that the agents had used to remember this system:
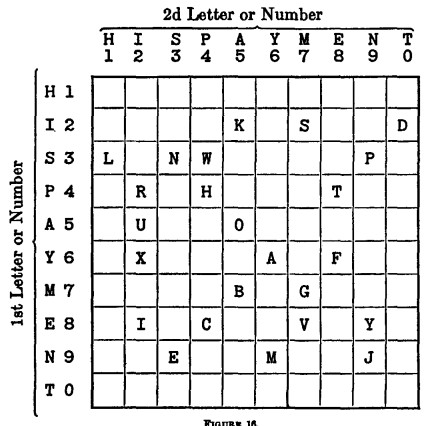
Beaird Glover wrote in his 1991 book Secret Ciphers of the 1876 Presidential Election:
“It is amusing to note that the conspirators selected as their key a phrase quite in keeping with their attempted illegalities — HIS PAYMENT — for bribery seems to have played a considerable part in that campaign.”
Assignment
You have to encode en decode messages using the ciphers that have been used by Samual Tilden’s campaign team. Encoding is done by replacing all letters in a message by bigrams composed of two uppercase letters. In encoding a message, no distinction is made between uppercase and lowercase letters, and all characters that are no letters of the alphabet are ignored.
A cipher key is composed of two components. The first component is a keyword containing different uppercase letters that are used to label the rows and columns of a square grid. In the following example, we have used the keyword ABCD.
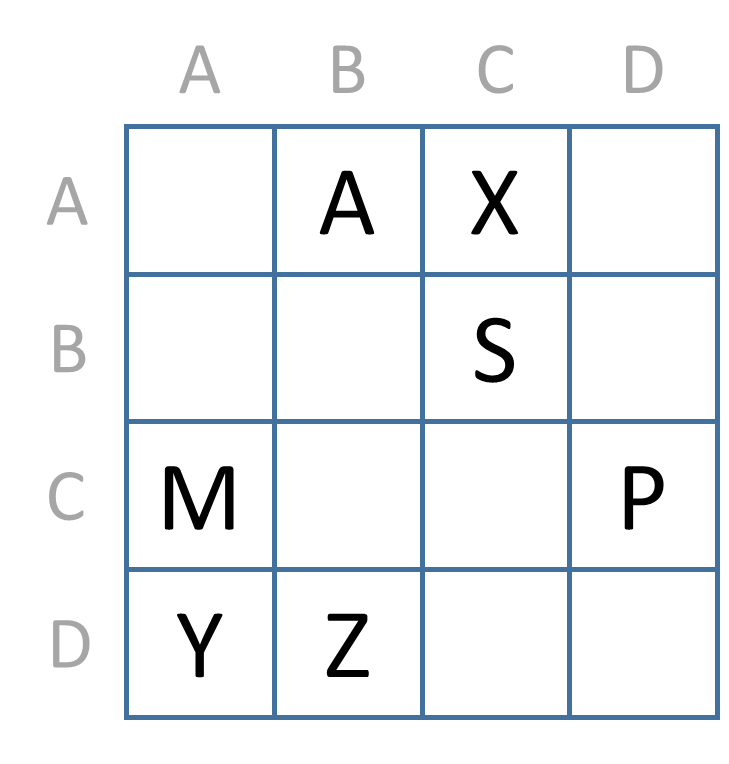
The second component is a description that indicates how a number of different letters of the alphabet have to be arranged in the square grid. Such a description alternates between sequences of successive capitals and natural numbers (that may contain multiple digits), and can start either with a capital or a natural number. The description is used to fill the square grid with the capitals included in the description. This is done by starting at the cell in the upper left corner. A capital indicates that the letter must be entered into the current cell. A natural number indicates that the corresponding number of cells must be skipped if we traverse the cells from left to right and from top to bottom. As such, the arrangement of the letters in the sample grid above corresponds to the description 1AX3S1M2PYZ. Note that after the final Z in the description we could have added another number 2 to indicate that the last two cells of the grid are empty, but this is optional.
You are asked to define a class Cipher. A keyword (String) and a description (String) must be passed upon initialization
of the objects of this class, which fixes the operation of the cipher. You may assume that only valid keywords and
descriptions are passed to the initialization method, without the need to explicitly verify this. The objects of this
class are immutable and must have the following properties:
-
A property
gridthat represents the square grid used by the cipher. This grid is represented as an array (Array) containing the rows of the grid (from top to bottom), where each row is itself represented as an array (Array) of characters (String; from left to right). The elements of each row are the capitals found in the corresponding cells of the grid, or a dash (-) in case the cell does not contain a capital. -
A property map that refers to an object (
Object) that maps each letter (String) from the grid onto the bigram (String) that is composed of the two letters used to respectively label the row and column where the letter is found in the grid.
In addition, the class Cipher must support at least the following methods:
-
A method
encodethat takes a message (String). The method must return the encoded message (String) obtained when applying the cipher. In encoding, only the letters in the given message are taken into account (all characters that are not letters are simply ignored), and no distinction is made between uppercase and lowercase letters. The returned encoded message only contains uppercase letters. In case the given message cannot be encoded based on the cipher used, anAssertionErrormust be raised with the messageinvalid message. -
A method
decodethat takes a message (String) that was encoded using the cipher represented by the object (cfr. methodencode). The method must return the letters (String) in the original message (all uppercase letters). In case the given message cannot be decoded using the cipher represented by the object, anAssertionErrormust be raised with the messageinvalid message.
Example
> let cipher = new Cipher("ABCD", "1AX3S1M2PYZ")
> cipher.grid
[["-", "A", "X", "-"], ["-", "-", "S", "-"], ["M", "-", "-", "P"], ["Y", "Z", "-", "-"]]
> cipher.map
{"A": "AB", "X": "AC", "S": "BC", "M": "CA", "P": "CD", "Y": "DA", "Z": "DB"}
> cipher.encode("spam")
"BCCDABCA"
> cipher.decode("BCCDABCA")
"SPAM"
> cipher.encode("eggs")
Traceback (most recent call last):
AssertionError: invalid message
> cipher.decode("BCCDBACA")
Traceback (most recent call last):
AssertionError: invalid message
> let cipher02 = new Cipher("HISPAYMENT", "14K1S2DL1NW4P2R1H3T3U2O6X3A1F6B1G4I1C2V1Y3E2M2J")
> cipher02.grid
[["-", "-", "-", "-", "-", "-", "-", "-", "-", "-"], ["-", "-", "-", "-", "K", "-", "S", "-", "-", "D"], ["L", "-", "N", "W", "-", "-", "-", "-", "P", "-"], ["-", "R", "-", "H", "-", "-", "-", "T", "-", "-"], ["-", "U", "-", "-", "O", "-", "-", "-", "-", "-"], ["-", "X", "-", "-", "-", "A", "-", "F", "-", "-"], ["-", "-", "-", "-", "B", "-", "G", "-", "-", "-"], ["-", "I", "-", "C", "-", "-", "V", "-", "Y", "-"], ["-", "-", "E", "-", "-", "M", "-", "-", "J", "-"], ["-", "-", "-", "-", "-", "-", "-", "-", "-", "-"]]
> cipher02.map
{"K": "IA", "S": "IM", "D": "IT", "L": "SH", "N": "SS", "W": "SP", "P": "SN", "R": "PI", "H": "PP", "T": "PE", "U": "AI", "O": "AA", "X": "YI", "A": "YY", "F": "YE", "B": "MA", "G": "MM", "I": "EI", "C": "EP", "V": "EM", "Y": "EN", "E": "NS", "M": "NY", "J": "NN"}
> cipher02.encode("Have Marble and Coyle telegraph for influential men from Delaware and Virginia.")
"PPYYEMNSNYYYPIMASHNSYYSSITEPAAENSHNSPENSSHNSMMPIYYSNPPYEAAPIEISSYESHAINSSSPEEIYYSHNYNSSSYEPIAANYITNSSHYYSPYYPINSYYSSITEMEIPIMMEISSEIYY"
> cipher02.decode("PPYYEMNSNYYYPIMASHNSYYSSITEPAAENSHNSPENSSHNSMMPIYYSNPPYEAAPIEISSYESHAINSSSPEEIYYSHNYNSSSYEPIAANYITNSSHYYSPYYPINSYYSSITEMEIPIMMEISSEIYY")
"HAVEMARBLEANDCOYLETELEGRAPHFORINFLUENTIALMENFROMDELAWAREANDVIRGINIA"
> cipher02.encode("Indications of weakening here.")
"EISSITEIEPYYPEEIAASSIMAAYESPNSYYIANSSSEISSMMPPNSPINS"
> cipher02.decode("EISSITEIEPYYPEEIAASSIMAAYESPNSYYIANSSSEISSMMPPNSPINS")
"INDICATIONSOFWEAKENINGHERE"
> cipher02.encode("Press advantage and watch Board.")
"SNPINSIMIMYYITEMYYSSPEYYMMNSYYSSITSPYYPEEPPPMAAAYYPIIT"
> cipher02.decode("SNPINSIMIMYYITEMYYSSPEYYMMNSYYSSITSPYYPEEPPPMAAAYYPIIT")
"PRESSADVANTAGEANDWATCHBOARD"