The second strand
Recall Watson and Crick's discovery of the following secondary structure for DNA that was introduced in "Counting DNA nucleotides":
-
The DNA molecule is made up of two strands, running in opposite directions.
-
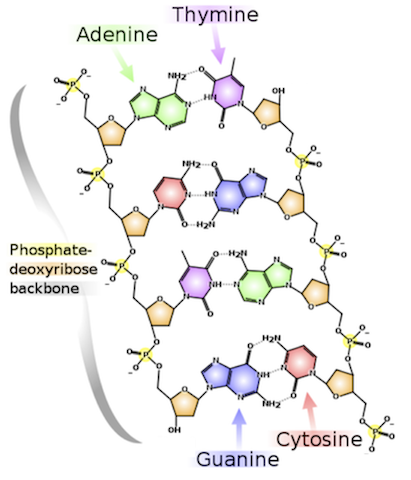
Each base bonds to a base in the opposite strand. Adenine always bonds with thymine, and cytosine always bonds with guanine. The complement of a base is the base to which it always bonds (see left figure below).
-
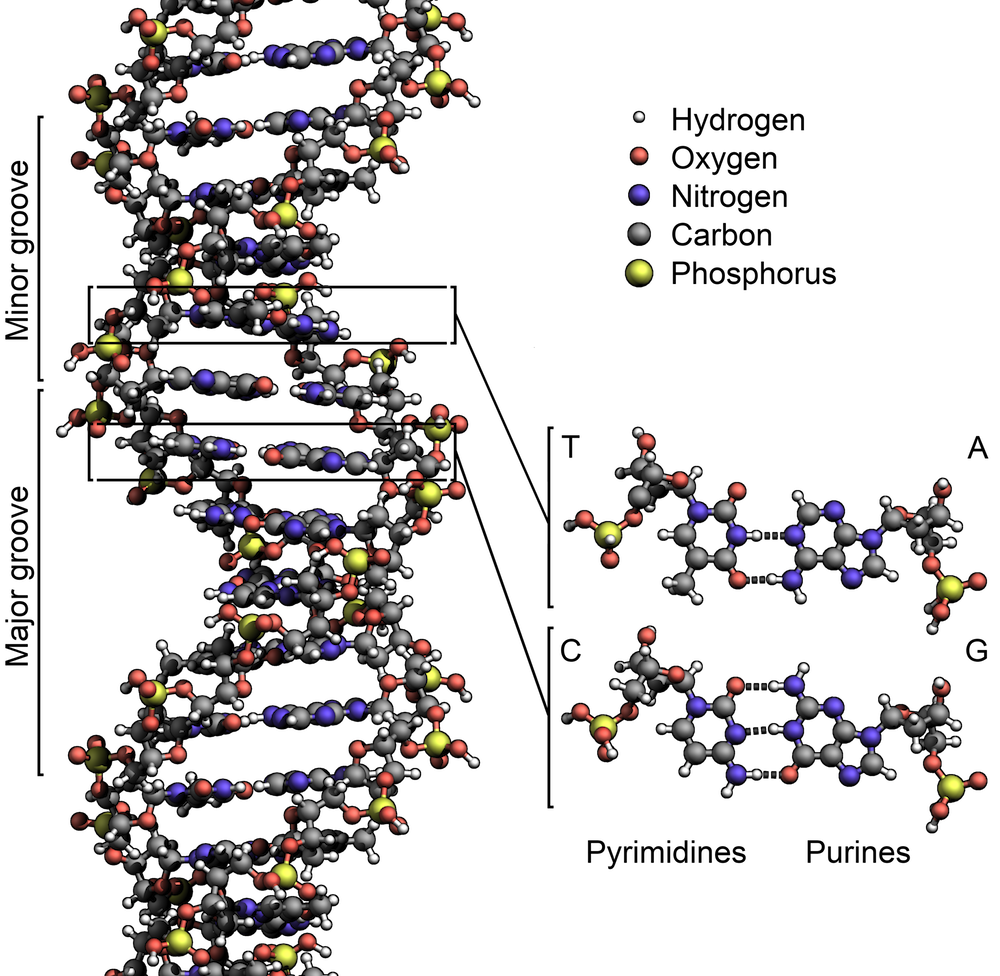
The two strands are twisted together into a long spiral staircase structure called a double helix (see right figure below).
Because genomic DNA is double-stranded, during sequence analysis we should examine both the given DNA string and its reverse complement.
Assignment
Recall that in a DNA string $$s$$, the bases A and T are complements of each other, as are the bases C and G. Furthermore, the reverse complement of $$s$$ is the string $$s'$$ formed by reversing the symbols of $$s$$ and then taking the complement of each symbol (e.g., the reverse complement of GTCA is TGAC).
A DNA string is called palindromic if it matches its reverse complement. Your task:
-
Write a function isPalindrome that takes a DNA string. The function must return a Boolean value that indicates whether or not the given DNA string is palindromic.
-
Write a function palindromes that takes the location of a FASTA file. The function must return an integer that indicates how many DNA strings in the given FASTA file are palindromic.
Example
In the following interactive session, we assume the FASTA file data.fna to be located in the current directory.
>>> isPalindrome('GATCGATGGGCCTATATAGGATCGAAAATCGC') False >>> isPalindrome('ATAT') True >>> isPalindrome(Seq('GCATA', IUPAC.unambiguous_dna)) False >>> palindromes('data.fna') 1
Programming shortcut
BioPython can also be used to take the reverse complement of a DNA string locally. Specifically, the complement() and reverse_complement() methods associated with Seq objects are suitable for this problem.
>>> from Bio.Seq import Seq >>> from Bio.Alphabet import IUPAC >>> seq = Seq('GATCGATGGGCCTATATAGGATCGAAAATCGC', IUPAC.unambiguous_dna) >>> seq Seq('GATCGATGGGCCTATATAGGATCGAAAATCGC', IUPACUnambiguousDNA()) >>> seq.complement() Seq('CTAGCTACCCGGATATATCCTAGCTTTTAGCG', IUPACUnambiguousDNA()) >>> seq.reverse_complement() Seq('GCGATTTTCGATCCTATATAGGCCCATCGATC', IUPACUnambiguousDNA())
The IUPAC.unambiguous_dna argument specifies that we are using the alphabet {A, C, G, T} and are not including the additional ambiguity symbols provided by IUPAC notation.
The EMBOSS package contains a program revseq that can be used to compute the reverse complement of a given DNA string.